Effective thermal management is crucial for the performance and longevity of electronic devices, especially those that generate significant heat, like CPUs, GPUs, and other high-performance components. Thermal pads and thermal gels are both commonly used materials to improve heat dissipation, but they serve different purposes and have distinct characteristics. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between thermal pads and thermal gels, helping you understand which is better suited for your application.
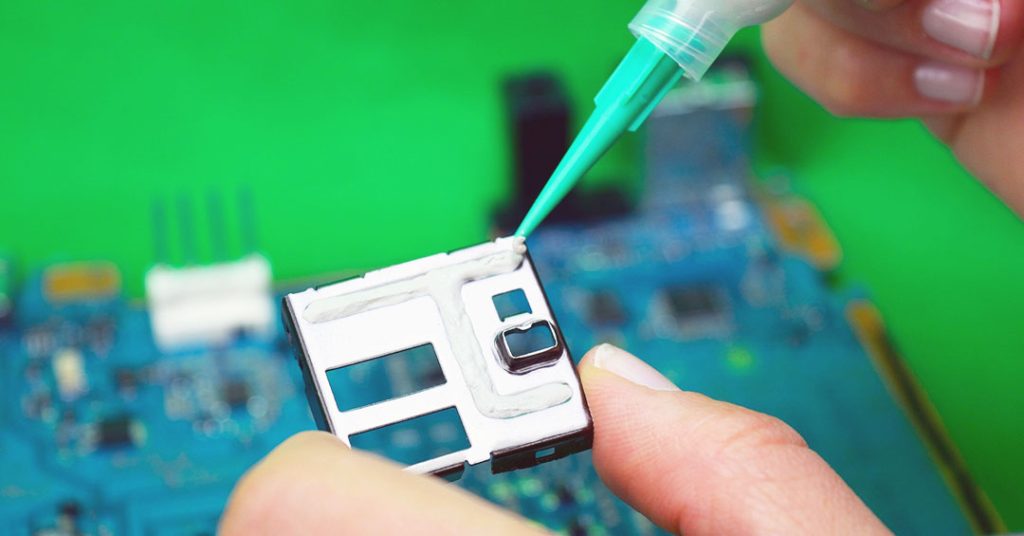
What are Thermal Pads?
Thermal pads are solid, flexible materials made from thermally conductive materials like silicone, rubber, or graphite. They are designed to fill the microscopic air gaps between a heat source and its heat sink, providing better thermal conductivity and improving heat dissipation. Thermal pads are pre-formed into various shapes, sizes, and thicknesses to fit specific components.
Key Features of Thermal Pads:
- Easy to Install: Thermal pads come in pre-cut shapes, so they’re easy to apply without the mess and complexity of spreading liquid compounds.
- Consistent Thickness: Pads maintain a consistent thickness, providing predictable thermal conductivity and gap filling.
- Durability: Unlike gels, thermal pads do not dry out or degrade as quickly. They provide long-term performance.
- Low Maintenance: Thermal pads require little maintenance compared to gels, which may need reapplication over time.
- Ideal for Large Surfaces: Thermal pads are effective for large contact areas or when the gap between surfaces is relatively large.
What are Thermal Gels?
Thermal gels, often referred to as thermal pastes or compounds, are soft, liquid-like materials designed to be applied between surfaces for effective heat transfer. Made from materials such as silicone or metal oxides, thermal gels fill the tiny gaps between two surfaces, ensuring optimal heat conductivity. They are typically used in high-performance applications where precise and efficient heat dissipation is necessary.
Key Features of Thermal Gels:
- Higher Thermal Conductivity: Thermal gels typically offer higher thermal conductivity than pads, which makes them suitable for high-performance devices.
- Customizable Application: Gels can be applied in a thin layer, allowing for precise and controlled application where required.
- Flexible: Unlike pads, thermal gels can fill even the smallest microscopic gaps, ensuring a better bond between components.
- Messier Application: The application of thermal gel requires care to avoid excess material spilling over the edges, making the installation process messier.
- Potential for Drying Out: Over time, thermal gels can dry out or harden, reducing their effectiveness, especially in high-heat environments.
Thermal Pads vs. Thermal Gels: Key Differences
| Feature | Thermal Pads | Thermal Gels |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower compared to gels, suitable for moderate heat | Higher thermal conductivity, ideal for high-performance |
| Ease of Application | Easy to apply, no mess | Requires careful application, can be messy |
| Durability | More durable, doesn’t dry out over time | Can dry out or degrade, requires reapplication over time |
| Best Use Case | Large surfaces or moderate heat applications | High-performance, small components like CPUs & GPUs |
| Cost | More affordable for mass production | Typically more expensive due to better performance |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, doesn’t need frequent reapplication | Needs periodic reapplication, especially in high-heat environments |
When to Use Thermal Pads?
Thermal pads are best suited for applications where:
- Heat dissipation is moderate: If the component generates only moderate heat, a thermal pad can do the job effectively.
- Large surface areas need coverage: Thermal pads are ideal for covering large contact areas with uneven surfaces, such as power supplies or large heatsinks.
- Ease of installation is a priority: If quick and easy installation is required, thermal pads are a great choice.
- Durability is important: For applications where long-term performance is needed without worrying about degradation, thermal pads are more reliable.
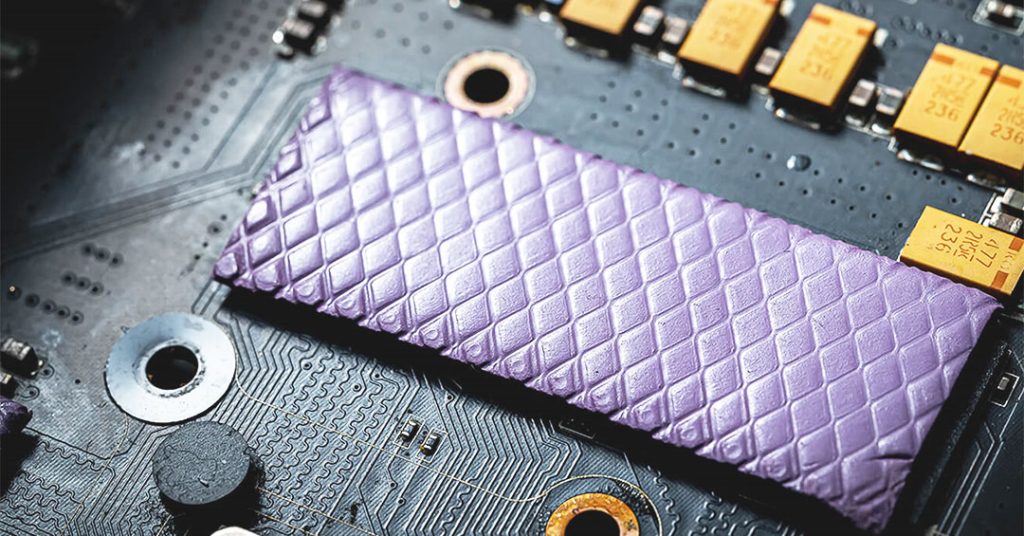

Common Applications of Thermal Pads:
- Power modules
- LED lighting systems
- Automotive electronics
- Consumer electronics like laptops and gaming consoles
- Memory chips and other large-area components
When to Use Thermal Gels?
Thermal gels are ideal for situations where:
- Maximum thermal conductivity is required: If your device operates at high heat levels (like overclocked CPUs, GPUs, or high-performance servers), thermal gels are the better option.
- Precision is important: Thermal gels are perfect for applications where fine control over the layer thickness is necessary to ensure optimal heat transfer.
- Small, delicate components need cooling: For smaller components with minimal space, thermal gels offer superior performance due to their ability to fill tiny gaps and imperfections.
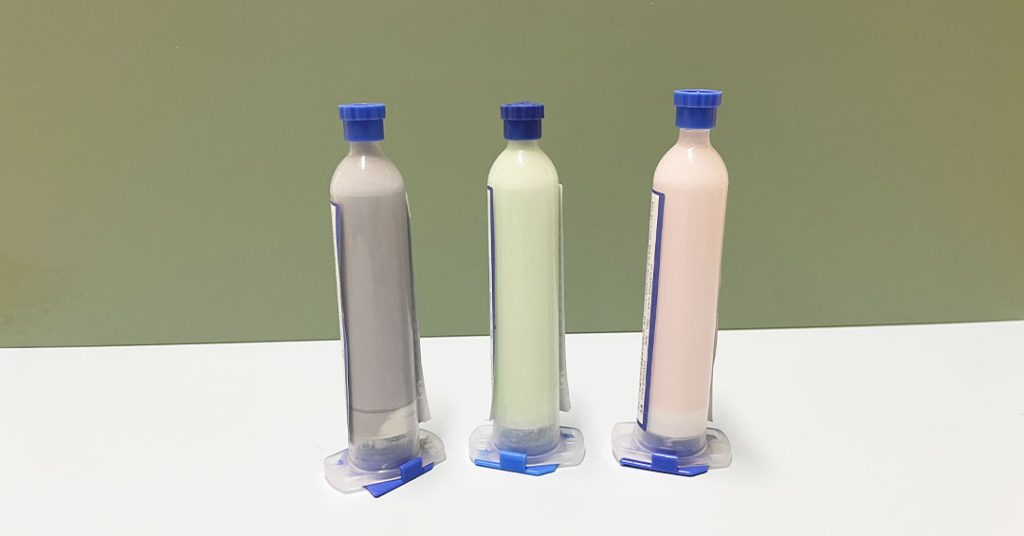

Common Applications of Thermal Gels:
- High-performance CPUs, GPUs, and gaming PCs
- Server processors and data centers
- Custom-built PCs and overclocked systems
- Specialized equipment that requires extreme cooling, like graphics workstations
Conclusion
The decision between thermal pads and thermal gels ultimately comes down to the specific needs of your application. Thermal pads are great for larger surfaces, easier installation, and moderate heat dissipation. On the other hand, thermal gels provide superior thermal conductivity and are better suited for high-performance devices and applications requiring precise thermal management.
By understanding the differences between these two materials, you can select the right solution for your thermal management needs. Whether you’re designing a high-performance computer or cooling automotive electronics, choosing the correct thermal material is crucial for optimal device longevity and performance.
If you need help deciding which material is best for your needs, feel free to reach out to our experts for guidance!